Google Analytics prohibits collecting personally identifiable information only.
It has been GA’s policy from the start. They don’t allow using any data you can use to identify a particular person.
What does it include?
The most important categories are email address, full name, home address, social security number, credit card details, and more.
In the following few paragraphs, we’ll talk more about:
- Why is prohibiting personally identifiable information (PII) now even more important than before?
- What does Google consider as PII, and what do they exclude?
- What happens if you (accidentally) collect personally identifiable information?
- How to avoid collecting personally identifiable information?
- How can I help you avoid getting into trouble?
So, let’s dive in.
Why is prohibiting personally identifiable information (PII) now even more important than before?
Privacy regulations are now on a much higher level than ever before, not only when it comes to Google Analytics. For example, things like GDPR in Europe or the Ecommerce directive require permission from the user to collect specific information.
So, Google was ahead of the curve with its regulations.
As a result, you need to be even more cautious about using identifiable information or any specific (marketing) purpose. If you have permission from the user to do that, then it’s okay.
What does Google consider as PII, and what do they exclude?
We mentioned a few categories in the introduction, but here is the (almost) complete list:
- full name
- username
- home address
- email address
- telephone number
- date of birth
- passport number
- fingerprint
- driver’s license number
- credit or debit card number
- Social Security number
- and more.
However, some categories meet all of Google’s requirements. Things like pseudonymous cookies and advertising IDs could be allowed.
For example, Google Analytics won’t prohibit sending an ad request with an IP address. Since IP addresses belong to the group of Google’s exclusions, you won’t break any prohibition policy.
But still, be careful. Data that Google might allow you could still be prohibited by GDPR, CCPA, or any other privacy legislation. The best example is that GDPR considers IP addresses as PII, which clearly shows that GA standards don’t necessarily match regulatory standards.
What happens if you (accidentally) collect personally identifiable information?
Let’s be perfectly honest – unless you’re highly cautious or already had a similar experience in the past, you might get into trouble by accidentally collecting PII.
From the Google perspective, since it’s against their terms and service, they can disable your Google Analytics account.
What’s even worse, that information could be present anywhere.
For example, it could be in the URL. If you send someone to a “Thank You” page, you can have their email in the URL, and you might end up having that information in Google Analytics, which ultimately leads to your account being disabled.
Another example would be form submissions. Once someone fills the form, you can get their email address, which can end up in Google Analytics and cause problems.
So, before implementing Google Analytics, you need to check every detail to ensure you’re safe.
How to avoid collecting personally identifiable information?
1. Limit the amount of data you collect
If you’re using tools such as Google Tag Manager, you can set up specific conditions that will successfully filter out this data before it comes to Google Analytics.
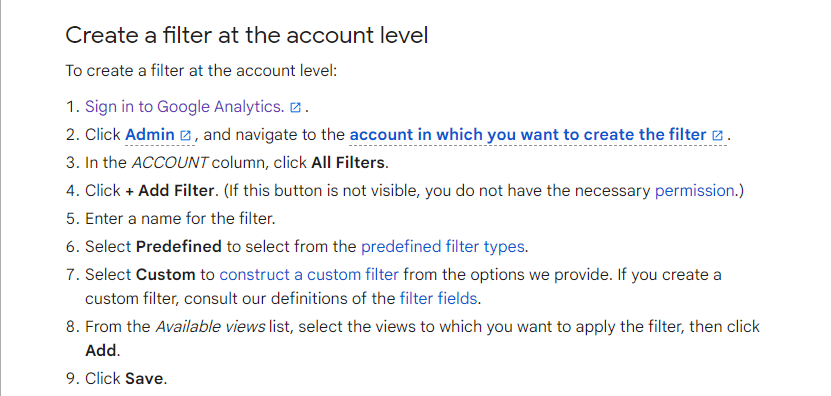
2. Setting up filters in GA
This one is pretty straightforward. I already stated the information you can’t collect in Google Analytics, and that’s precisely what you need to filter out. Don’t hesitate to contact us if you still have trouble doing it yourself.
3. Delete specific users from your system
You can consider this approach as your last resort. Google Analytics has a specific alphanumeric database identifier for deleting users, which lets you remove particular users.
Of course, before starting the whole process, you have to know which users (or groups of users) could potentially represent a problem for you.
4. Analytics.js code
Adding analytics.js code before the URL arrives in GA is another excellent way of protecting yourself. This code removes the personally identifiable information instead of you.
It’s an easy way to make sure that URLs won’t have any personal data.
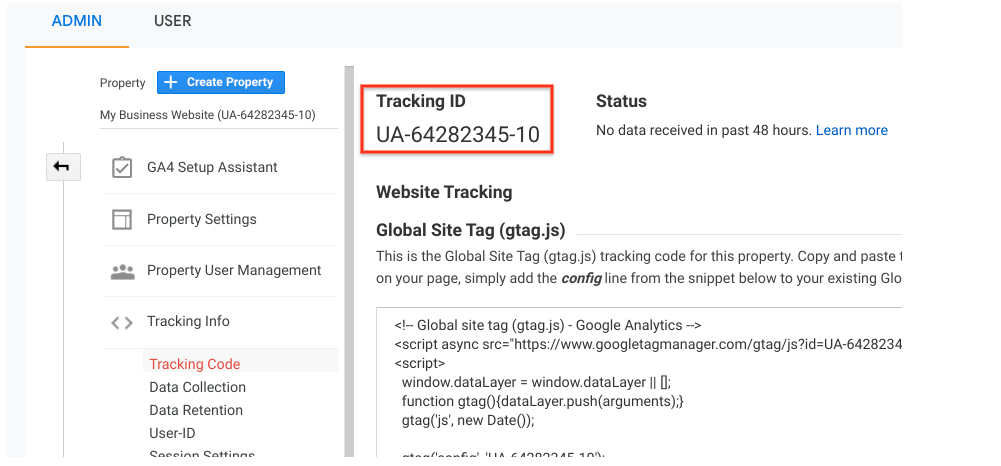
5. Importing your data the right way
It’s crucial how you import data to Google Analytics. It has to be free of PII.
On top of that, that data mustn’t contain device identification, such as a mobile phone’s unique device identifier. It’s pretty important to remember.
Google’s team explained the whole process.
6. Location data
Make sure that your location data does not include GPS. Google Analytics won’t allow it since they anticipate it as personally identifiable information.
Also, avoid the so-called “fine-grained location” information.
How can I help you avoid getting into trouble?
Let’s face it – using Google Analytics properly is not the easiest task in the world.
I mentioned all the possible ways to avoid collecting personally identifiable information but still, you might find it daunting doing it all by yourself.
Besides all my regular duties, as your data analytics consultant, I can also help you protect your GA account from collecting PII.
Usually, I consider all the solutions mentioned above, but every client’s situation is different. For example, in your case, it might be enough to set up filters in GA properly, and that’s it.
Still, the whole process starts with our conversation. I first consider your current business goals and the problems you face. After that, I go to the next step – finding the best solutions for your situation, including choosing the best ways to protect you from collecting PII.
You can schedule a free strategy call with us with no hard strings attached.
Final verdict
So, what can you draw out from this article?
- Collecting PII is now even more dangerous than it was.
- Google considers many categories as PII, but they also exclude a few things.
- Google can simply disable your account if they find out you’re collecting PII.
- There are several ways to avoid collecting PII.
- Professional help can get you out of trouble.












