In our previous article, we listed things that google analytics can do to help you get started. I got a lot of questions from folks that had similar questions for google tag manager.
Some were confused if GTM is a replacement for good old GA, others wondered what does GTM do if you already have analytics. I have tried to put this to rest with things google tag manager can and can’t do.
- What Does Google Tag Manager Do?
- Setup GA & Adwords
- Add Conversion Pixels
- Re-use the same information multiple times
- Imporove Your Site Speed
- Easily add code on multiple pages
- Test pixels before putting them live
- Maintain history of all changes
- Roll back to a previous step
- Advanced Tracking
- Help you configure tags yourself
- Add user permissions
- Use built-in templates
- Manage all tags at one place
What Does Google Tag Manager Do?
1. Setup GA & AdWords
One of the first and essential things google tag manager can do is allowing you to deploy google analytics using universal analytics tag. This is important in the sense that you won’t need to add any extra code to your website except tag manager container snippet.
If you are still using both codes on your website, the best practice is to remove google analytics code snippet and install google analytics via tag manager.
Furthermore, you can also set up AdWords remarketing in tag manager.
2. Add conversion pixels (e.g FB)
The next enormous thing you can do in google tag manager is to simply add the third party conversion pixels. This enables you to add all conversion measurements at a single place.
third party conversion pixels
3. Re-use the same information multiple times
Tag manager offers the opportunity to create reusable user-defined variables, which in return prevents errors and saves time. Some of the popular GTM variables are auto-event variable, data layer variable and 1st party cookie variable.
You can learn in depth about variables here.
4. Improve your site speed
Inserting multiple code snippets on your website and calling each snippet to an external file results in a low page speed.
Google tag manager improves your site speed by firing tags asynchronously. It means a tag is fired whenever it is ready and it does not wait for others to load first.
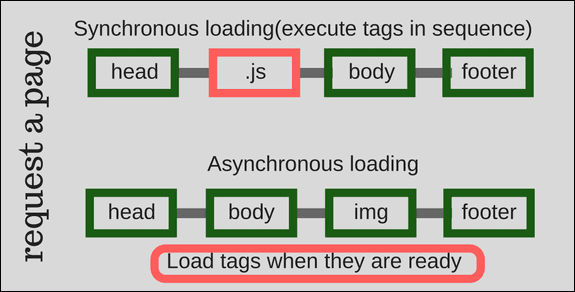
how tag manager deals with tags
The second reason why GTM improves your site speed is it calls external resources once. It offers a single container tag to control all tags on your site. In conclusion, GTM reduces the number of calls to external resources and hence improve your site speed.
5. Easily add code on multiple pages
You can insert GTM tags on multiple pages without actually interacting with your website. This reduces the need for a developer to change your site code every time you need. You can get this done by yourself once you understand how google tag manager works.
6. Test pixels before putting them live

tag manager test & debug
The awesomeness of google tag manager lies in its test and debug feature.Every time you create a new tag, you can test and preview it before setting it live.This help you find the errors and fix them before it is implemented on your site.
7. Maintain history of all changes
Google tag manager keep the history of activities that are carried out in any workspace. You can view the activity history for any workspace by clicking the activity history at the bottom of the workspace.
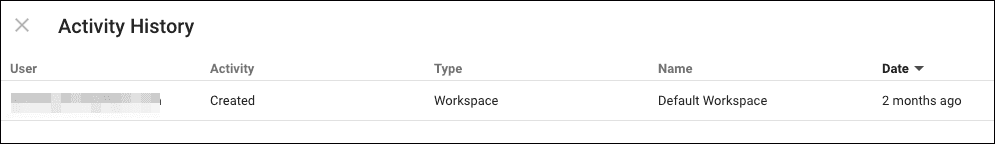
activity history
Whenever you make any changes in Google Tag Manager, it allows you to decide whether you want to create a version or not. If you choose to create a version, the current draft will become the current version and it will start visible to all users. This way tag manager keeps the history of changes.
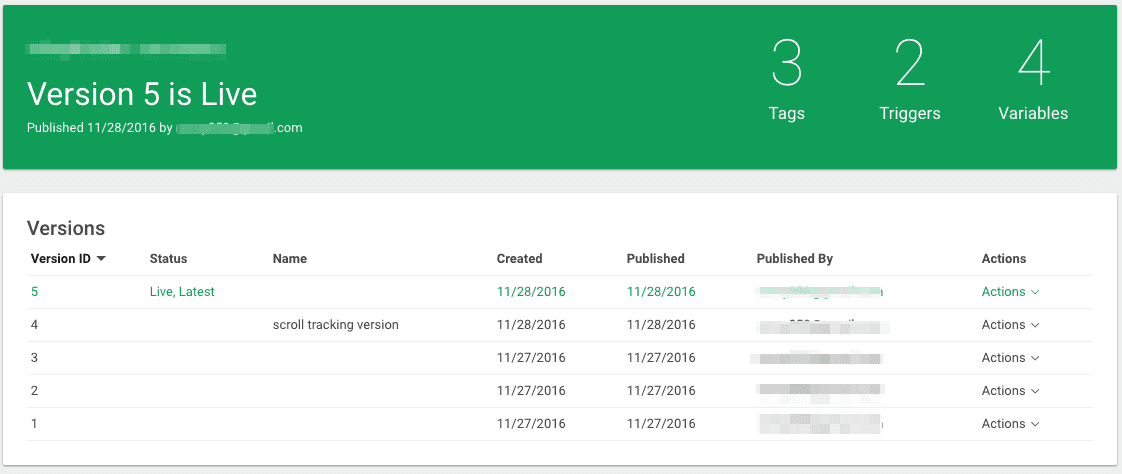
tag manager versions
8. Roll back to a previous step
Every time you edit or change something in tag manager, it records the change and the user who made it. If you decide to keep the change you can create a new version. By doing this, GTM keeps the history of changes you have done and enables you to roll back to an older setup.
publish previous version
9. Advanced tracking
With the built-in GTM tags, you can set up advanced tracking in a short amount of time. Some of the advanced trackings you can do are form tracking and tracking all outbound links on your site. If you do this manually without GTM, it would generally take longer to accomplish.
10. Help you configure tags yourself
Google tag manager is not a complex tool and does not need a specific person to use it. Once you get your hands dirty with the basics, you can create and manage tags by yourself. This in return allows you to stop bothering your developer less often and let them focus on other things that matter.
11. Add User Permissions
Google tag manager enables you to give access to other people at account and container level. This way multiple users can work on the same account and you can see what other users have done.
12. Use built-in templates
Google tag manager has already provided a handful of built-in tags for your ease.This feature helps you create a tag using a template instead of copying and pasting code. You just have to add a few details to the template and it will automatically generate code.
13. Manage all tags at one place
When you are dealing with multiple tags, especially when they are not triggered from a single place, chances are you might feel exhausted and disturbed switching from place to place.
While google tag manager provides a flexible platform to manage all the tags at a single place and trigger them whenever you want.
What Google Tag Manager Cannot Do?
1. See reports about user engagement
Google tag manager is not a reporting tool. So, you will always need google analytics or another tool to be connected with tag manager to see reports.
2. Tags associated with in-page structure
Google tag manager should not be used for things that impact in-page structure such as social sharing widgets (addthis) or things that change the design of the page. It’s best for things that run in the background and are not visible to the user.
3. Remember what a user did on the last page and visit
GTM has no memory. By default, it has no idea what activity user has done in the past be it the last page or last visit. For anything you want to remember and reuse later you need to store it using cookies, local storage or your own backend and send it to GTM when needed.
4.Tags that need to be loaded right away
Google tag manager load tags asynchronously, which means a tag is fired whenever it is ready. In most cases, it helps improve site speed but on the other side, you can’t use it to add stuff like A/B testing code. These scripts must be loaded right away.
Final Thoughts:
If you have stepped into the world of digital analytics, you must not underestimate the power of tag manager. And if you are already convinced, I have covered how to migrate to GTM here.













